A passionate advocate for justice and fair compensation, Richard Norris founded ClaimSettlementPros to create a trusted platform that simplifies and demystifies the claim settlement process....Read more
Car accidents are a common occurrence on the roads, and they can have devastating effects on the body. One of the most severe injuries that can result from a car accident is brain damage. But can a car accident really cause brain damage?
The answer is yes. Car accidents can cause various types of brain injuries, ranging from mild concussions to severe traumatic brain injuries. These injuries can have long-lasting effects on a person’s cognitive, emotional, and physical abilities, making it crucial to seek medical attention immediately after a car accident. Let’s dive deeper into the topic of car accidents and brain damage, and understand how they are linked.
Car accidents are one of the leading causes of brain damage. Even minor collisions can result in traumatic brain injuries (TBIs). Symptoms of a TBI may not appear until days or weeks after the accident and can include headaches, dizziness, and memory loss. It’s important to seek medical attention immediately after an accident to rule out any potential brain injuries.
Can a Car Accident Cause Brain Damage?
Car accidents are one of the leading causes of traumatic brain injuries (TBI). In fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), motor vehicle accidents account for about 14% of all TBIs in the United States. While not all car accidents result in brain damage, the risk is always present, and it is important to understand the potential consequences of a car accident.
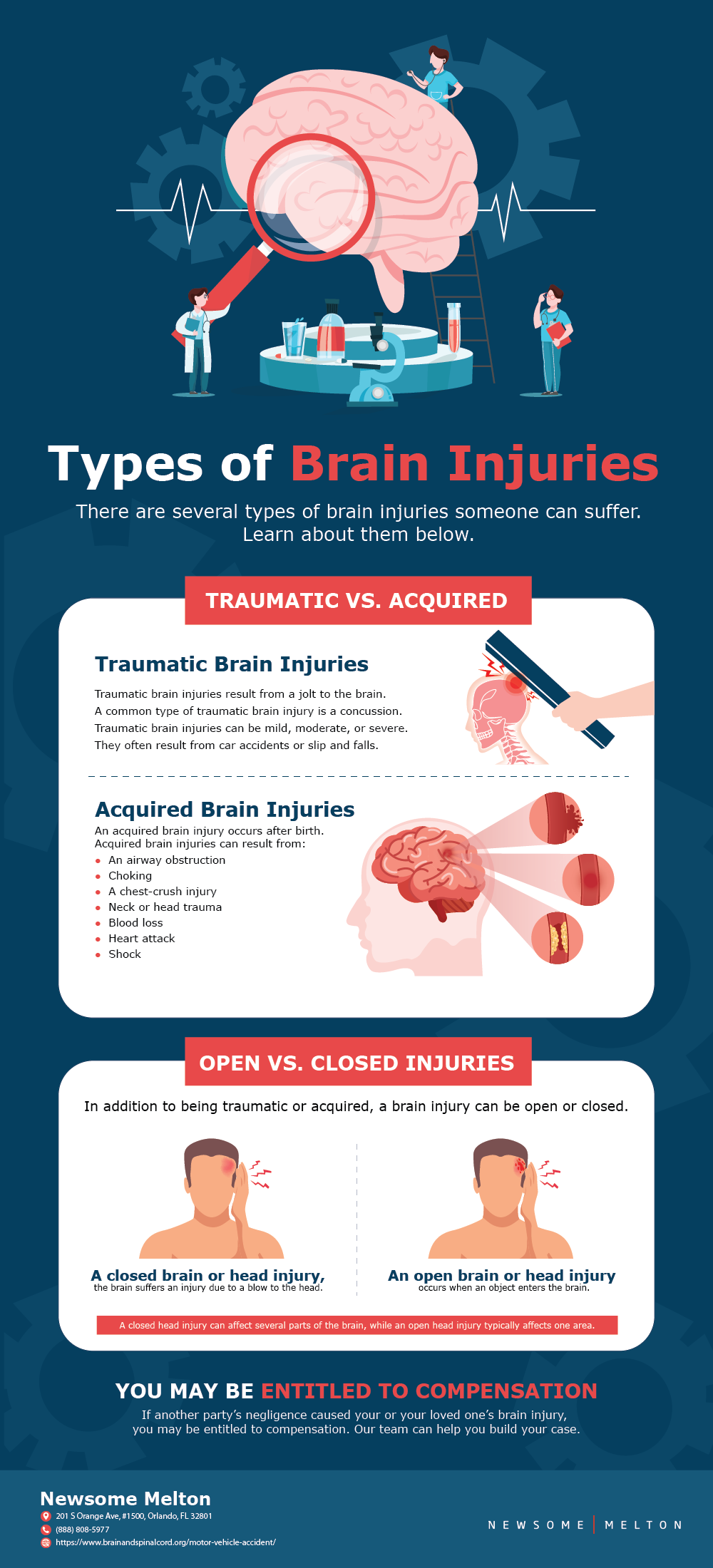
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
A traumatic brain injury occurs when an external force causes damage to the brain. This can happen in a variety of ways, including a blow to the head, a sudden jolt, or a penetrating injury. In the case of a car accident, a TBI can occur from the impact of the collision, even if the person’s head does not hit anything.
The severity of a TBI can vary widely. Mild TBIs, often referred to as concussions, may cause short-term symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and confusion. However, more severe TBIs can cause long-term or permanent damage, including cognitive impairments, behavioral changes, and physical disabilities.
Types of Brain Injuries That Can Result From a Car Accident
Car accidents can cause a variety of brain injuries, depending on the force and direction of the impact. Some of the most common types of brain injuries that can result from a car accident include:
- Concussions
- Contusions
- Coup-contrecoup injuries
- Diffuse axonal injuries
Concussions are the most common type of TBI and are often referred to as mild TBIs. They occur when the brain is jolted or shaken inside the skull, causing temporary dysfunction. Contusions are bruises on the brain tissue and can occur when the brain hits the skull. Coup-contrecoup injuries occur when the brain hits one side of the skull and then rebounds and hits the other side. Diffuse axonal injuries involve damage to the brain’s axons, which are responsible for transmitting signals between neurons.
Long-Term Effects of Brain Injuries
The effects of a brain injury can be long-lasting and may impact a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks, hold a job, or maintain relationships. Some of the long-term effects of a brain injury may include:
- Cognitive impairments, such as memory loss or difficulty concentrating
- Behavioral changes, such as irritability or depression
- Physical disabilities, such as impaired vision or hearing
- Changes in personality or social behavior
In some cases, the long-term effects of a brain injury may not become apparent until months or even years after the accident. It is important for anyone who has been in a car accident to seek medical attention, even if they do not immediately experience symptoms of a brain injury.
Preventing Brain Injuries in Car Accidents
While it is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of brain injury in a car accident, there are steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk. These include:
- Wearing a seatbelt
- Using car seats or booster seats for children
- Ensuring that airbags are functioning properly
- Driving defensively and obeying traffic laws
- Avoiding driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol
By taking these steps, individuals can reduce their risk of a brain injury in a car accident.
Conclusion: The Risks of Brain Injury in Car Accidents
Car accidents can have serious and long-lasting consequences, including traumatic brain injuries. While not all car accidents result in brain damage, the risk is always present, and it is important to take steps to minimize that risk. If you or a loved one has been in a car accident, it is important to seek medical attention, even if there are no immediate symptoms of a brain injury. By taking proactive steps to prevent brain injuries, individuals can help protect themselves and their loved ones from the potentially devastating consequences of a car accident.
Contents
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is brain damage and how does it occur in car accidents?
- What are the signs and symptoms of brain damage after a car accident?
- How is brain damage diagnosed after a car accident?
- What are the treatment options for brain damage after a car accident?
- Can brain damage after a car accident be prevented?
Frequently Asked Questions
Car accidents can cause a range of injuries, including brain damage. Here are five common questions about the link between car accidents and brain damage.
What is brain damage and how does it occur in car accidents?
Brain damage refers to any injury that causes damage to the brain tissue. In a car accident, brain damage can occur when the head hits a hard surface or when there is a sudden jolt to the head and neck area. This can cause the brain to move around inside the skull and result in bruising, bleeding, or swelling.
Brain damage can also occur if there is a lack of oxygen to the brain, which can happen if the accident causes the airway to become blocked or if there is a drop in blood pressure.
What are the signs and symptoms of brain damage after a car accident?
The symptoms of brain damage after a car accident can vary depending on the extent and location of the injury. Common signs and symptoms include headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, fatigue, and changes in mood or behavior. In severe cases, there may be seizures, loss of consciousness, or paralysis.
If you or someone you know has been involved in a car accident and is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
How is brain damage diagnosed after a car accident?
Brain damage is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, imaging tests such as CT scans or MRI scans, and neurological assessments. These tests can help identify any structural damage to the brain, as well as any changes in cognitive function or behavior.
It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible after a car accident to ensure that any potential brain damage is diagnosed and treated promptly.
What are the treatment options for brain damage after a car accident?
The treatment options for brain damage after a car accident depend on the extent and location of the injury. In mild cases, rest and monitoring may be sufficient. However, in more severe cases, surgery or other medical interventions may be necessary to reduce swelling, prevent further damage, or repair any structural damage to the brain.
Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, may also be needed to help the individual recover from any cognitive or physical deficits caused by the brain injury.
Can brain damage after a car accident be prevented?
While it is not always possible to prevent brain damage in a car accident, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of injury. Wearing a seatbelt and using appropriate child safety seats can help prevent head injuries in the event of an accident. Avoiding distracted driving, following traffic laws, and avoiding driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol can also help reduce the risk of car accidents and the associated risk of brain damage.
If you or someone you know has been involved in a car accident and is experiencing symptoms of brain damage, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
In conclusion, it is evident that car accidents can indeed cause brain damage. The force of impact during a collision can cause the brain to jolt within the skull, leading to traumatic brain injuries. These injuries can range from mild concussions to severe brain hemorrhages that can cause permanent damage. It is crucial to seek medical attention immediately after a car accident, even if you do not have any visible injuries.
Prevention is always better than cure. Therefore, it is essential to take necessary precautions while driving. Always wear a seatbelt and ensure that all passengers in the car do the same. Avoid distractions such as using your phone while driving, eating, and drinking while behind the wheel. Also, ensure that you obey traffic rules and follow speed limits to avoid accidents.
In conclusion, car accidents can have catastrophic consequences, including brain damage. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize safety and take necessary precautions while driving to ensure that you and your passengers remain safe. Seek medical attention after an accident, even if you feel fine, and follow the advice of your healthcare provider to prevent any long-term damage.
A passionate advocate for justice and fair compensation, Richard Norris founded ClaimSettlementPros to create a trusted platform that simplifies and demystifies the claim settlement process. With over two decades of experience in the legal and insurance industries, Richard has amassed a wealth of knowledge and insights that inform our strategy, content, and approach. His expertise is instrumental in ensuring our information remains relevant, practical, and user-friendly.
More Posts

